Please note: a valid prescription is required for all prescription medication.
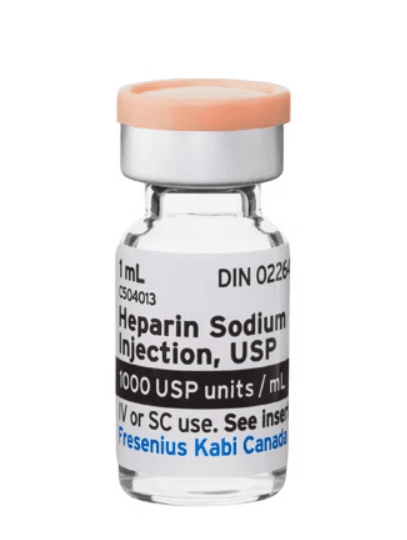
Heparin Vial for Anticoagulation
Buy More, Save More: Get 20% off when you buy 3 or more of any one product using code LESS20 at checkout.
Applies to all products originating from Canada. Maximum allowable quantity equal to a 90-day supply per single order.
Price range: $105.99 through $120.99
Secure Encrypted Payments
Heparin is an anticoagulant used to prevent and treat blood clots. Hospital teams and outpatient clinics use it when fast-acting blood thinning is required. This page helps you compare options, understand safe use, and see how to order a heparin vial without insurance with US delivery from Canada.
What Heparin Is and How It Works
This anticoagulant reduces the blood’s ability to clot by enhancing antithrombin activity. It acts quickly and can be adjusted or reversed in supervised settings. Clinicians use it during procedures, after certain surgeries, and for the initial management of venous thromboembolism. Border Free Health connects U.S. patients with licensed Canadian partner pharmacies; prescriptions are verified with prescribers before dispensing.
Heparin interrupts parts of the coagulation cascade. The effect starts shortly after injection when given intravenously. Subcutaneous use provides a slower onset for prevention in some settings. Monitoring strategies can include lab tests when therapeutic dosing is used; your clinician decides if and how to monitor.
For more background on conditions where anticoagulation matters, see Blood Clot DVT PE and Cardiovascular. If your care relates to heart attacks and stents, review Acute Coronary Syndrome.
Who It’s For
This medicine is used to prevent or treat blood clots in adults under a prescriber’s direction. It is commonly used around surgeries, during hospital care, and when oral options are not suitable. It may also be used to help keep intravenous lines open at low doses when ordered.
People with active bleeding, a history of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia, or severe platelet problems should avoid it. Caution applies with recent brain, eye, or spinal surgery, or with uncontrolled high blood pressure. Your healthcare professional will decide if this therapy fits your situation. For rhythm-related stroke prevention context, see Atrial Fibrillation.
Dosage and Usage
Use this medicine exactly as prescribed. Hospitals often give intravenous boluses and infusions for treatment courses. Preventive regimens commonly involve subcutaneous injections on a regular schedule. The order may differ based on your diagnosis and other medicines.
If you receive a heparin injection vial, a clinician or trained patient caregiver draws the dose with a sterile syringe. Rotate injection sites if using subcutaneous doses. Follow aseptic technique and the label’s instructions for single-dose or multi-dose containers. Do not make dose changes on your own; defer to the official label and your prescriber.
Strengths and Forms
Vials come as single-dose preservative-free and multi-dose preserved presentations. Concentrations and vial sizes vary by manufacturer. Common options include 10 mL and 30 mL containers for clinical use. Many institutions stock standard concentrations suitable for prevention or treatment regimens.
For example, a heparin 5000 unit vial is a frequent option in many facilities. Availability may vary by lot and supplier. Your pharmacist may dispense an equivalent presentation based on your prescription and current supply.
Missed Dose and Timing
If you miss a preventive dose, contact your care team for guidance. Timing matters with anticoagulants. Do not double up to make up a missed injection unless your prescriber instructs you to. If you use infusion therapy, follow facility protocols for restarts or adjustments.
Keep a log of doses and times. Use reminders to help maintain consistency. For catheter flush orders, follow your institution’s protocol to avoid unintended systemic dosing.
Storage and Travel Basics
Store vials at room temperature as directed on the official label. Keep them in the original carton to protect from light. Do not freeze. Once a multi-dose heparin vial is opened, follow the labeled beyond-use timeframe; discard any remaining solution after that period. Single-dose containers should be used once and discarded.
Keep out of reach of children and pets. When traveling, carry this therapy in original packaging with your prescription label. Pack syringes and swabs in a dedicated kit. Place the medicine in your carry-on. If you travel frequently, ask your clinician for documentation to ease security checks. Airlines may have specific rules for sharps.
Pen Handling and Sharps Disposal
This product is supplied for syringe use rather than a prefilled pen. Use new sterile needles and syringes for each injection. Place used needles and syringes in an FDA-cleared sharps container. If one is not available, use a heavy-duty puncture-resistant container with a secure lid. Follow local regulations for disposal or ask your pharmacist about take-back options.
Benefits
This class provides rapid anticoagulation and flexible dosing. Clinicians can adjust infusions quickly in hospital settings. Reversal with protamine is available when medically necessary. The treatment is often used when oral anticoagulants are not appropriate, such as around procedures or during acute illness. It can support line patency at low doses when ordered.
Side Effects and Safety
- Bleeding or bruising
- Injection site pain, redness, or irritation
- Mild elevations in liver enzymes
- Skin reactions at the injection site
Serious risks include major bleeding and heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Rarely, prolonged use may affect bone health. Hyperkalemia can occur in susceptible patients. Seek emergency care for signs of severe bleeding, sudden shortness of breath, chest pain, new neurologic symptoms, or signs of an allergic reaction. Your clinician may order lab monitoring in therapeutic scenarios.
Drug Interactions and Cautions
Using this therapy with other agents that affect clotting can increase bleeding risk. Examples include aspirin, NSAIDs, P2Y12 inhibitors, other anticoagulants, and certain herbals such as ginkgo, garlic, and high-dose fish oil. Tell your prescriber about all medicines and supplements you take.
Special cautions apply with spinal or epidural procedures due to the risk of epidural hematoma. Discuss timing and risk mitigation with your care team. Benzyl alcohol in preserved multi-dose vials is not appropriate for neonates. For condition education, see Acute Coronary Syndrome ACS.
What to Expect Over Time
With intravenous use, anticoagulant effects begin quickly and wear off after infusion stops. Subcutaneous prevention regimens provide steady coverage when doses are consistent. Your clinician may check labs to guide adjustments if you are on a therapeutic protocol. Most people will not feel different day to day; adherence and monitoring support safe outcomes.
Keep track of injections, infusion rates, and any bruising or bleeding. Report nosebleeds, gum bleeding, or black stools promptly. Wear a medical ID if you receive ongoing anticoagulation.
Compare With Alternatives
Low molecular weight heparins offer once or twice daily injections in many cases. Consider Lovenox Injections when a prescriber recommends that option. For oral maintenance in suitable patients, warfarin is a long-standing choice; see Warfarin. Some patients transition to direct oral anticoagulants after stabilization, as appropriate.
Pricing and Access
We aim to make care more affordable with Canadian sourcing and transparent information. If you are comparing options, ask our team about heparin vial cost and available presentations. We offer US shipping from Canada with secure payment and encrypted checkout. To check current availability or discounts, visit Promotions. Your final out-of-pocket amount depends on the vial size, concentration, and the supplier that fills your prescription.
Availability and Substitutions
Supply can vary by manufacturer and lot. If a specific vial is not available, a pharmacist may coordinate an equivalent presentation with your prescriber. Where appropriate, a preservative-free heparin vial may be selected for single-use situations. Your clinician’s order determines the exact product dispensed.
Patient Suitability and Cost-Saving Tips
This therapy may be suitable when a fast, adjustable anticoagulant is needed. It is often selected in hospital care, during procedures, and when oral options are not feasible. Patients with a history of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia, active bleeding, or severe thrombocytopenia generally should not receive it.
To manage costs, ask about multi-month supplies when clinically appropriate, and coordinate refills to reduce separate fees. Combine medicines in one shipment when possible. Use reminders to avoid lapses. If your care plan changes, your prescriber can adjust to a different anticoagulant that best fits your needs and budget.
Questions to Ask Your Clinician
- Why is this anticoagulant preferred for my condition?
- Will I need lab monitoring, and how often?
- How long will I need injections or an infusion?
- What signs of bleeding should I report right away?
- Which other medicines or supplements should I avoid?
- Should I use single-dose or multi-dose vials for my plan?
- How should I time doses around procedures or dental work?
Authoritative Sources
Ready to order? Start your request for an Inviclot vial or the prescribed presentation today with prompt, express shipping. Ships from Canada to US. Prescription required; temperature-controlled handling when required. This page is educational and does not replace your clinician’s advice.
Express Shipping - from $25.00
Shipping with this method takes 3-5 days
Prices:
- Dry-Packed Products $25.00
- Cold-Packed Products $35.00
Shipping Countries:
- United States (all contiguous states**)
- Worldwide (excludes some countries***)
Standard Shipping - $15.00
Shipping with this method takes 5-10 days
Prices:
- Dry-Packed Products $15.00
- Not available for Cold-Packed products
Shipping Countries:
- United States (all contiguous states**)
- Worldwide (excludes some countries***)
What is Heparin used for?
Heparin is an anticoagulant used to prevent and treat blood clots, including deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism. It is also used in hospitals to prevent blood clot formation in patients undergoing surgery or dialysis. Heparin works by inhibiting clotting factors in the blood, reducing the risk of dangerous clots forming.
How is Heparin administered?
Heparin is typically administered via intravenous (IV) or subcutaneous injection by a healthcare professional. The dosage is carefully monitored using blood tests to ensure the correct balance between preventing clots and avoiding excessive bleeding.
Can Heparin cause excessive bleeding?
Yes, because Heparin is a blood thinner, it increases the risk of excessive bleeding. Patients should be monitored for signs such as unusual bruising, prolonged bleeding from cuts, dark stools, or blood in urine. If any of these occur, seek medical attention immediately.
What should I do if I miss a dose of Heparin?
If you receive Heparin in a medical setting, missed doses are rare. However, if self-administering, contact your doctor for instructions. Never take an extra dose to compensate for a missed one, as this can increase bleeding risk.
Are there dietary restrictions while taking Heparin?
There are no strict dietary restrictions, but patients should avoid excessive alcohol and discuss with their doctor before taking supplements such as vitamin K, fish oil, or herbal products that can affect clotting.
What’s the difference between single-dose and multi-dose vials?
Single-dose vials are preservative-free and intended for one-time use, then discard. Multi-dose vials contain a preservative that allows multiple withdrawals under sterile technique. Your prescriber or pharmacist will choose based on your plan, setting, and age. For neonates and some pediatric patients, preservative-free options are often preferred. Follow the label’s beyond-use dates and dispose of opened containers when they expire.
Can I self-inject this medicine at home?
Some patients are trained to inject subcutaneous doses at home when the prescriber deems it appropriate. A nurse or pharmacist can teach technique, site rotation, and safe handling of sharps. Intravenous treatment is typically managed in clinical settings. Never adjust your own dose or schedule without guidance. Keep supplies organized and use a log to track each injection.
What is heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT)?
HIT is an immune-mediated reaction that can lower platelets and increase clot risk. It usually occurs after exposure to heparin products. Clinicians diagnose it with clinical scoring and confirmatory testing. If suspected, the medicine is stopped and an alternative anticoagulant may be started. Tell your care team if you have a history of HIT so they can avoid re-exposure and plan a safe alternative.
How is dosing monitored?
Monitoring depends on the indication and route. For therapeutic infusions, clinicians may use lab tests to guide adjustments. Preventive subcutaneous doses may not require routine lab checks, depending on protocols. Your care team will decide the right approach and communicate any testing schedule to you. Report bleeding or new symptoms promptly so your plan can be reviewed.
Can I take pain relievers while on this therapy?
Some pain relievers increase bleeding risk when used with anticoagulants. NSAIDs and certain antiplatelet agents may add risk. Acetaminophen is often preferred for pain or fever, but always check with your prescriber or pharmacist. Provide a full list of medicines and supplements so they can screen for interactions and help you choose safer options.
What if I’m pregnant or breastfeeding?
This anticoagulant has long clinical use during pregnancy when an injectable option is appropriate. Your obstetric and medical teams will coordinate dosing and monitoring. If breastfeeding, discuss timing and formulation details with your clinician. Avoid preserved multi-dose vials for neonates. Decisions should be individualized based on risks, benefits, and your medical history.
How should I store opened vials and supplies?
Keep vials at room temperature as directed on the label and protect from light. Single-dose vials should be used once and discarded. Opened multi-dose containers must be discarded after the labeled timeframe, even if some solution remains. Keep syringes, swabs, and sharps containers together in a clean kit. Store everything out of reach of children and pets.
Rewards Program
Earn points on birthdays, product orders, reviews, friend referrals, and more! Enjoy your medication at unparalleled discounts while reaping rewards for every step you take with us.
You can read more about rewards here.
POINT VALUE
How to earn points
- 1Create an account and start earning.
- 2Earn points every time you shop or perform certain actions.
- 3Redeem points for exclusive discounts.
How to book an appointment
- 1Create Begin by completing a profile or log into your existing account. This step ensures we have the necessary information to provide you with a service that's tailored to your needs. account and start earning.
- 2Scheduling an appointment with our online booking system is easy. Pick a day and time that suits you. You’ll receive an immediate confirmation, without the wait.
- 3Discuss your concerns and symptoms and receive a thorough diagnosis from one of our licensed doctors during a confidential video appointment.
- 4If you've been prescribed medication, your Rx is sent directly to one of our licensed pharmacies and delivered right to your door.
Get Started
To book an online doctor appointment, register for an account or login. After doing so, you can book your visit on this page.