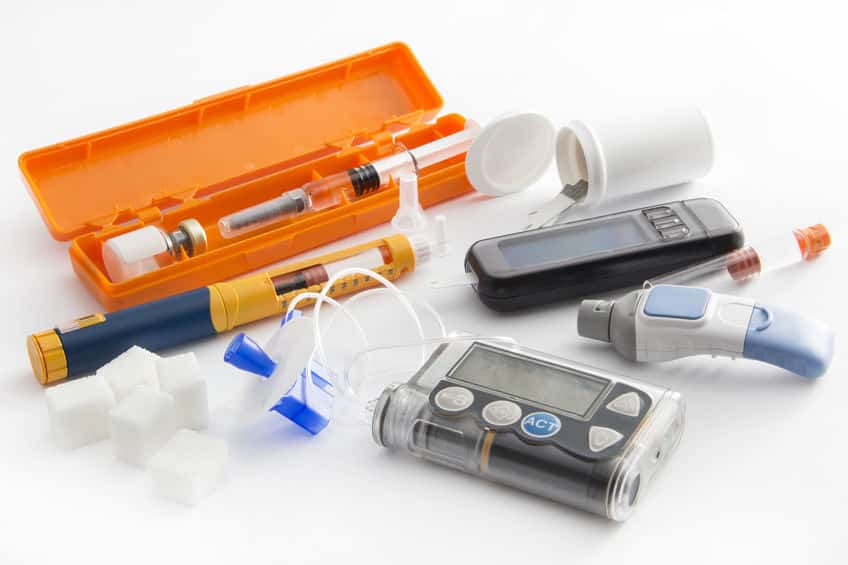
Living with type 1 means learning new skills, building routines, and staying flexible. This guide explains core elements of type 1 diabetes treatment with plain language and practical context. You will see how insulin options, monitoring tools, nutrition, and safety planning fit together day to day.
Key Takeaways
- Insulin basics: basal and bolus work together to manage glucose.
- Devices help: CGMs and pumps can reduce daily burden.
- Safety first: hypoglycemia and ketones need clear plans.
- Personalization matters: treatment targets vary by age and context.
What Makes Type 1 Different from Type 2?
Type 1 is an autoimmune condition where the immune system destroys pancreatic beta cells. People require lifelong insulin to replace what the body no longer makes. Type 2 primarily involves insulin resistance (reduced response to insulin) and gradual secretory decline. These distinct mechanisms shape targets, risks, and medications.
Understanding the difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes helps families and clinicians avoid unsafe assumptions. For example, ketosis risk is higher in type 1, so pump interruptions need quick action. In newly diagnosed adults, antibody testing and C-peptide can clarify the picture. For a plain-language overview of pathophysiology and symptoms, see this NIDDK overview of type 1.
Type 1 Diabetes Treatment
Most people use a basal-bolus insulin plan. Basal insulin (background insulin) covers 24-hour needs, while rapid-acting bolus insulin (mealtime insulin) addresses food and corrections. Matching insulin to food, activity, stress, and illness is an ongoing process. Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) can guide adjustments between visits.
Insulin type, timing, and delivery method should reflect your goals, daily life, and safety profile. To compare insulin classes and onset/peak profiles, see our concise primer on Types of Insulin for quick reference during clinic discussions. When discussing basal choices, the Lantus Insulin guide explains long-acting properties, while Fiasp Rapid-Acting Insulin outlines mealtime kinetics and use cases.
Insulin Delivery Options and Devices
Multiple daily injections (MDI) remain a reliable approach, especially with pens. Pens can simplify dosing and reduce injection discomfort. For people using pens, reviewing needle size and technique helps reduce bruising and lipohypertrophy (fatty tissue changes). Many find smaller-gauge needles improve comfort and consistency.
Some choose a type 1 diabetes insulin pump to automate basal delivery and enable precise boluses. Patch-style and tubed systems now integrate with CGMs, offering automated adjustments and hypo-protection features. Discuss cannula length, infusion set change intervals, and travel backup plans with your clinic team. For pen users, the NovoPen 4 can provide dependable dosing; for comfort and technique, see BD Nano Pro Pen Needles to understand needle specifications and fit.
Pumps and Patch Systems
Pumps allow flexible basal patterns for dawn phenomenon, shift work, or menstruation-related variability. Hybrid closed-loop algorithms use CGM data to adjust basal delivery and may reduce low and high glucose time. Still, success depends on infusion set care, accurate carb entries, and consistent sensor wear. People should carry backup pens and basal insulin for downtime or device failure.
If you are comparing pump features, ask about algorithm behavior, sensor compatibility, activity modes, and ketone protocols. For foundational details on pump use and safety signals, NIDDK’s page on insulin pumps offers a succinct, balanced summary; consider the context provided here: insulin pump basics.
Monitoring, Targets, and Safety
Monitoring includes fingersticks, CGM data, and periodic lab work. Practical targets balance safety with quality of life. Discuss A1C goals, time in range, and hypoglycemia thresholds with your team. Glucose meters remain useful for calibration, backup, and ketone-related checks. The FreeStyle Freedom Lite Meter can serve as a simple backup device; for lancing technique and site rotation, review Contour Microlet Lancets for lancet size and compatibility details.
Ranges and targets differ by clinical context, and the type 2 diabetes range is not always a suitable comparator for type 1. Consider illness, pregnancy, age, and hypoglycemia unawareness when tailoring goals. Keep ketone strips on hand when glucose rises or you feel ill. Clear sick-day rules and glucagon preparation can prevent emergencies. Document contact pathways for after-hours questions and device alarms.
Nutrition, Activity, and Sick-Day Planning
Food plans should respect culture, preference, and budget. Carbohydrate counting is common, while some use simplified meal patterns or fixed carb ranges. Protein and fat can impact glucose later, so some people pre-bolus or split doses to match digestion. Exercise improves insulin sensitivity (the body’s response to insulin) but can raise or lower glucose depending on type, timing, and intensity.
There is no evidence that can type 1 diabetes be reversed with diet and exercise. However, thoughtful nutrition and regular activity can reduce swings, improve energy, and support heart health. Build an exercise routine with pre- and post-activity checks, carbs-on-board strategies, and reduced overnight basal if advised. For handling insulin resistance and training days, our guide on How to Treat Insulin Resistance explains practical levers you can discuss with your clinician.
Tip: Create a brief sick-day card listing insulin doses, correction rules, ketone steps, and emergency contacts. Keep a photo on your phone for quick reference.
Diagnosing and Early Management
Symptoms often include thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, and weight loss. In adults, diagnosis may be less obvious. Clinicians may order antibodies (GAD, IA-2, ZnT8) and C-peptide to assess insulin production. Early education about hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), glucagon, and ketone checks can prevent serious events. Families benefit from hands-on practice with pens, sensors, and meters before leaving clinic.
Clear pathways reduce confusion when questions arise later. Ask your team to outline how to diagnose type 1 diabetes in adults, especially if autoimmune markers are borderline or presentation is atypical. For foundational context on classification, see our explainer Breaking Down the Types of Diabetes, which frames key distinctions used in clinic.
Guidelines and Care Team
Shared decision-making is central. Individual goals often reflect life realities: school, work shifts, mental health, pregnancy, or coexisting conditions. Regular follow-up allows fine-tuning insulin-to-carb ratios, correction factors, and basal settings. People should also review driving safety, travel supplies, and sick-day protocols at least yearly.
Care plans should align with type 1 diabetes treatment guidelines, including screening for complications and psychosocial support. For consensus-driven targets and monitoring intervals, the ADA Standards of Care provide annually updated recommendations that clinicians use to guide care. For additional lived-experience insights and news, explore our Type 1 Diabetes category, which aggregates practical posts you can share with family members.
Why Treatment Plans Differ by Type
Medication choices, targets, and safety strategies vary by diabetes type. Insulin is mandatory in type 1 because the pancreas stops producing it. In type 2, many people start with lifestyle changes and non-insulin medicines, then add insulin if needed. These differences explain why family members with different types may compare notes but follow distinct instructions.
Understanding type 2 diabetes treatment can clarify discussions at mixed-type support groups. Some medicines that help with weight or heart risk in type 2 are not indicated for type 1. For an overview of non-insulin options and their roles, see our explainer on Jardiance Uses for context about cardiovascular benefits and glucose effects in adults.
Building a Supportive Toolkit
Reliable supplies and backup tools reduce stress. Keep an extra meter, strips, lancets, and low-glucose treatments in work or school bags. Rotate injection sites and change infusion sets on schedule. When using pens, check device compatibility before clinic visits to simplify training and troubleshooting.
If you rely on pens for daily care, consider how device ergonomics affect dosing. Reviewing a device like the NovoPen 4 can help you discuss grip and memory functions with your educator. For meter-based backups, pair the FreeStyle Freedom Lite Meter with appropriate strips, and review lancet sizing using Contour Microlet Lancets so fingersticks are consistent and comfortable.
Recap
Type 1 care evolves with your life. Insulin, monitoring, nutrition, and safety planning work best as a coordinated system. Small adjustments made thoughtfully can prevent big swings and reduce stress. Keep asking questions, keep notes, and revisit goals as your needs change.
This content is for informational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional medical advice.